Market Games
THE PRODUCT
Image sensors are devices made from silicon chips that capture photons and convert the photons into electrons to display optical information (i.e. images). It is used in a variety of devices. Most notable are digital cameras and mobile phones. It is produced in a semiconductor Fabrication plant ("Fab" or "Fab Plant") from silicon wafers.Silicon Wafer
Image Sensor Chip
PRODUCT FEATURES
Resolution
Resolution is the fineness of details in an image. High resolution sensors are small sensors with high pixel count, which means the pixel has to be smaller. The smaller the pixels, the higher the resolution (the finer the details you can capture in an image). Mobile customers want image sensors with high resolution because 1) smartphones need small sensors and 2) smartphone customers want high resolution pictures. For auto customers, having a high resolution is not that important as fine details of the image is not as important as image detection.Sensitivity
Light sensitivity is a measure of the minimum amount of light needed to generate an electronic signal. Reducing pixel sizes (increasing the resolution), reduces light sensitivity, which has consequences both for high and low levels of scene luminance and for short and long exposure duration. For Auto image sensors, this increases safety risks. For example, when driving in fog or darkness, an image sensor with low light sensitivity might not be able to detect objects correctly. See picture below: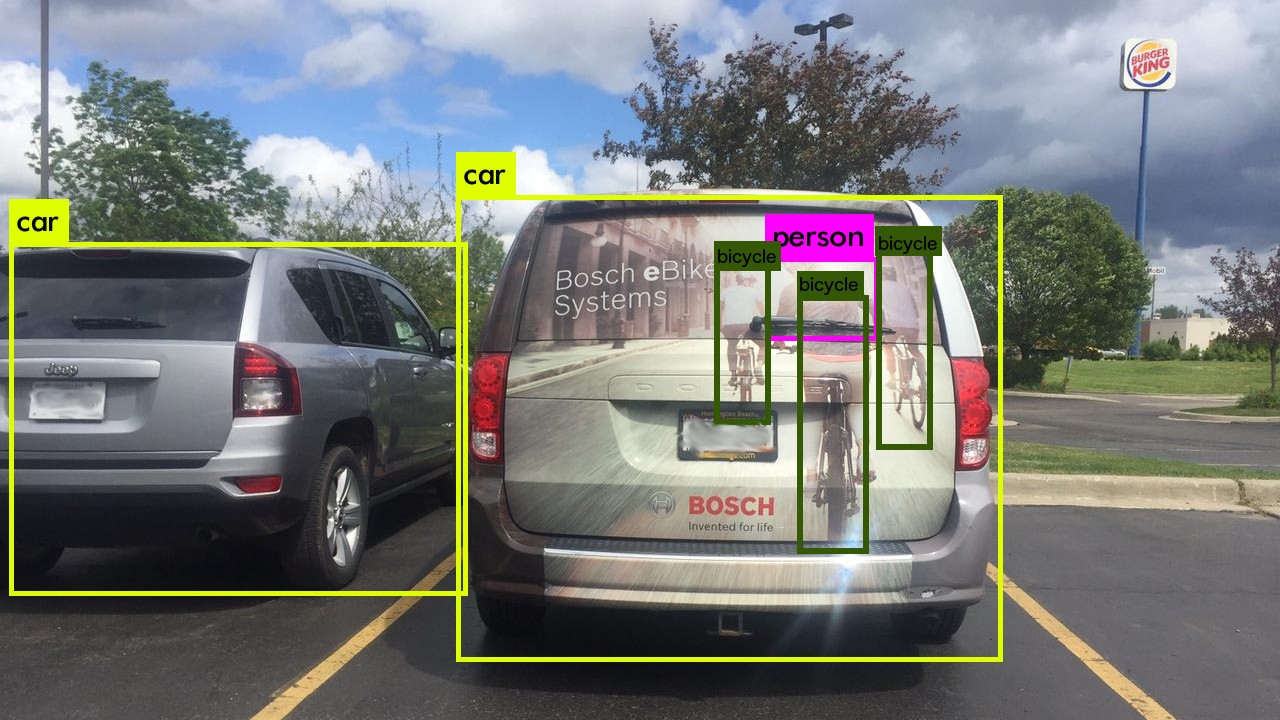
The downsides are, when the light sensitivity is high (larger sensor with larger pixel sizes), that resolution and power consumption suffer. These are not negative factors for mobile sensors.
Power
Power refers to the power efficiency of the sensor (the higher the power consumption, the lower the power efficiency). Power consumption of the sensor impacts the battery life of a mobile phone. Therefore the mobile customers require power efficient image sensors. On the other hand, power efficiency is not a critical product feature for auto customers.Temperature Range
Temperature range measures a sensor's ability to perform in extreme temperatures, which is an essential feature for auto sensors. This is a minor factor for mobile sensors as smartphones are not exposed to extreme temperatures in the way that vehicles are.Product Feature Ranking System
Product Features, Development Time, and Research and Development (R&D) Cost
Another impact of the product development time is, it impacts the product release date. For example, if your product release date is July 1, then you can’t start production until that date. As a result, your production volumes will only be 50% of the annual capacity.Exhibit 2 provides the expected research and development cost at different quality levels (different ranks for each product feature).
